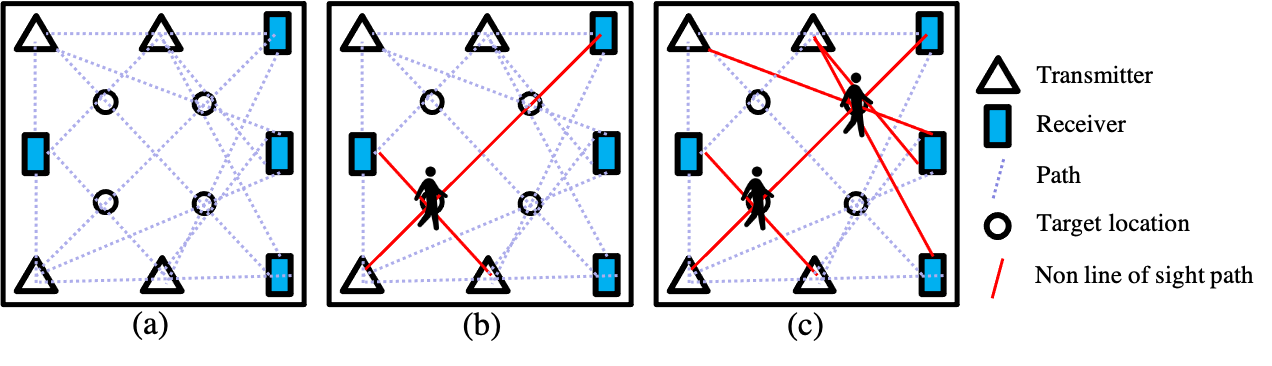
Currently, there is an increasing demand for technology that enables localization without possessing the devices such as smartphones.
Up to now, device-free indoor localization has been performed using data such as video and thermal images, but there are still problems that they include a lot of privacy information other than position information.
Therefore, many methods using radio waves are currently being researched as device-free localization considering privacy. This can be said to solve the privacy issue because it is not possible to infer other personal information by observing the signal characteristics of radio waves. However, most methods use special information such as the frequency, phase, and phase difference of Wi-Fi signals called Wi-Fi CSI (Channel State Information), so there are difficulties to use them in the real world.
In this project, as a new device-free indoor localization method, we proposed a device-free multi-person indoor localization method using Wi-Fi RTT [1]. RTT (Round Trip Time) is a protocol that performs distance measurements using the communication time of Wi-Fi signals. It is a technology that has begun to attract attention in recent years for indoor localization of devices. The proposed technology is a new application of the Wi-Fi RTT protocol and expands the possibilities of RTT, which has been focused only on the positioning of devices.
However, Wi-Fi radio waves are susceptible to the effects of multipath in the environment, and noise processing is an issue. Therefore, in this project, we also proposed a device-free indoor localization method using UWB [2]. UWB (Ultra Wide Band) is well known as a radio wave that is strong against multipath, and it is possible to measure distance based on communication time like Wi-Fi. We confirmed that this proposal improves the localization accuracy compared to the method using Wi-Fi RTT [1].
In addition, compared with the existing device-free indoor localization method using Wi-Fi RSSI [4], we confirmed that both methods using Wi-Fi RTT [1] and UWB [2] can perform localization with high accuracy [3].
In this project, in an environment where multiple radio transceivers and receivers are installed, we constructed an indoor localization system that utilizes changes in radio wave conditions caused by people obstructing their communications. In this system, it is possible to realize the localization of multiple people by learning only the data where one person is in the environment.
Publications
Wi-Fi RTTを用いたデバイスフリー複数人屋内測位
情報処理学会研究報告 第67回UBI合同研究発表会, オンライン開催, 9 2020. [2]野村 篤史,須ヶ﨑 聖人,坪内 孝太,西尾 信彦,下坂 正倫.
UWBの測定距離と直接波の減衰度を利用したデバイスフリー複数人屋内測位
情報処理学会研究報告 第74回UBI研究発表会, 福岡県北九州市 及びオンライン開催(ハイブリット形式), 6 2022. [3]Atsushi Nomura, Masato Sugasaki, Kota Tsubouchi, Nobuhiko Nishio, Masamichi Shimosaka.
Device-free multi-person indoor localization using the change of ToF, The 21st International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom 2023)
–Related work–
[4]M. Youssef, M. Mah, and A. Agrawala, Challenges: device-free passive localization for wireless environments. In Proceedings of the 13th annual ACM international conference on Mobile computing and networking (MobiCom 07)