In Wi-Fi fingerprint-based indoor localization, we need to acquire a dataset with a high-density dataset in the target environment in this framework.
To overcome the data acquisition cost problem, we propose a brand new data augmentation for Wi-Fi indoor localization named Between-Location data augmentation (BL data augmentation).
BL data augmentation generates the fingerprint data for the whole target environment with high density by only using the sparsely sampled data.
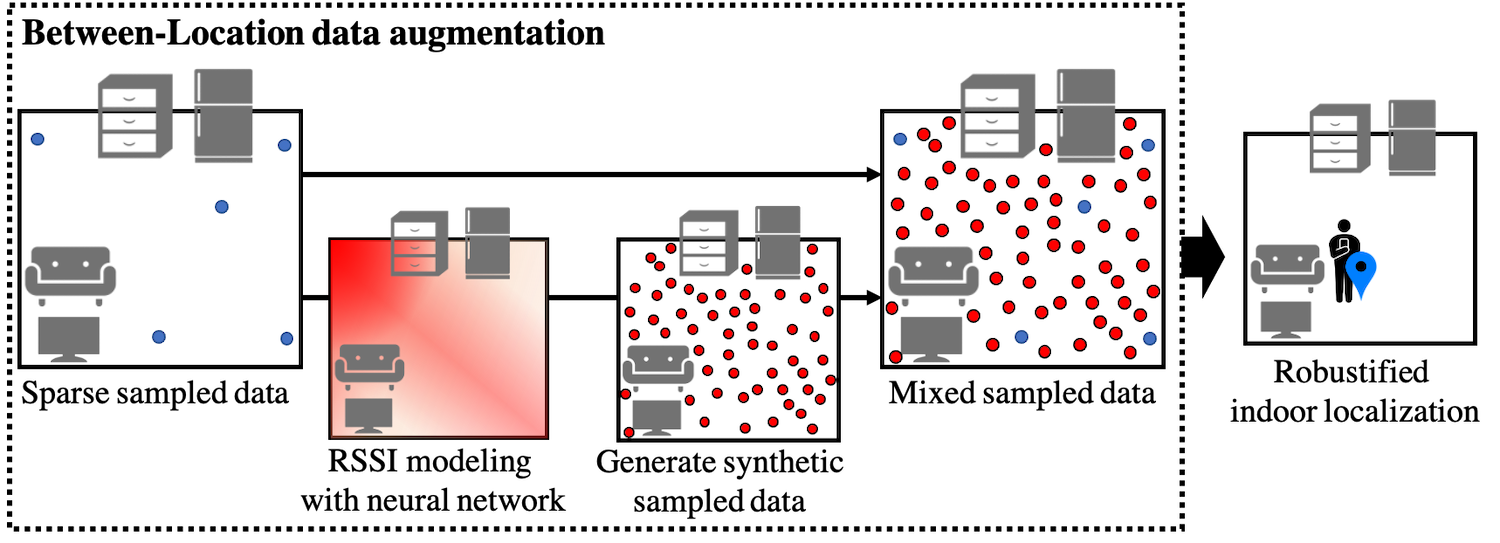
Between-Class learning, which is the origin of BL data augmentation and the latest powerful data augmentation method for sound recognition and image processing, mixes two data linearly with normalization; however, this mixing does not make sense in indoor localization because mixed fingerprint has no meaning and the label of indoor localization is not categorical information but physically correlated information. To overcome these two problems, we propose the generative model based on neural networks installed the physical relationship of labels and Wi-Fi fingerprint property.
This data augmentation drastically enables us to reduce data sampled locations while keeping the localization accuracy even if some target locations have no data.
From the experimental results, the localization with BL data augmentation using 10 % sampled location achieves the same accuracy with localization without data augmentation using all sampled locations.
—– Publication —–
M. Sugasaki and M. Shimosaka,
“Robustifying Wi-Fi localization by Between-Location data augmentation,”
IEEE Sensors Journal, doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3106765.